Recommendations for vascular protection. Address:
- A - A1c
- B - Blood pressure
- C - Cholesterol
- D - Drugs to protect
- E - Exercise/healthy Eating
- S - Smoking cessation
Related:
Recommendations for Vascular Protection. Address:
A1c
Usually ≤ 7.0%. See Targets and Priorities page for exceptions. Optimal glycemic control has been shown to significantly reduce major vascular events. See the A1c page for more information.
Blood Pressure
BP target < 130/80 mmHg (threshhold for both treatment and target)
- Diabetes Canada 2018 guidelines are now harmonized with Hypertension Canada guidelines.
- Advise patient to have blood pressure checked at least once a year and more often if elevated.
- Patients are encouraged to check their blood pressure at home. See Topics Catalogue: Vascular Risk for patient resources.
- ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitors and ARBs (angiotensin receptor blockers) are first line treatment for hypertension in those patients who have diabetes, known cardiovascular disease (CVD) and/or renal disease (including increased urinary albumin excretion).
- ACE inhibitors, ARBs, dihydropyridine CCBs (calcium channel blockers) or thiazide/thiazide-like diuretic medications may be used as first line treatment for hypertention in those patients who have diabetes without known CVD or renal complications.
- Multiple antihypertensive medications may be required to achieve target.
Cholesterol
The lipid panel consists of TC (Total Cholesterol), LDL-C, HDL-C, Triglycerides and non-HDL-C. Apo-B requires a separate order. Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines suggest that people with diabetes have lipids tested every 1-3 years or more often based on cardiovascular risk. Lipids can be checked at the lab in a non-fasting state if no known TG abnormalities.
Cholesterol is essential to body function as it forms membranes for cell walls, is used to make horomones and forms bile acids. A small amount of cholesterol moves through the body through lipoproteins (LDL, HDL, VLDL). Lipoproteins are comprised of cholesterol, triglycerides, protein and phospholipid molecules.
| Definition | Target for Diabetes | Treatment | |
Cholesterol or TC
|
Cholesterol or Total Cholesterol: The sum of all cholesterol
|
No set target
|
|
LDL-C
|
Low Density Lipoprotein Sometimes called 'bad' or 'lousy' cholesterol Contributes to atherosclerosis at high levels |
< 2.0 mmol/L or > 50% reduction from baseline (Some physicians are not using LDL targets alone and are assigning medications based on CV risk factors present) |
|
apo-B
|
Apolipoprotein-B is the main protein component of the atherogenic lipids -LDL, VLDL (Very Low Density Lipoprotein) and IDL (Intermediate Density Lipoprotein) Useful to measure when TG is elevated (>4.5 mmol/L) as LDL cannot be calculated |
< 0.8 g/L
|
|
HDL-C
|
High Density Lipoprotein Somtimes called 'good' or 'healthy' cholesterol Carries excess cholesterol to the liver for disposal Considered when looking at overall CV risk but not a target of therapy |
No specified target (Generally >1.0mmol/L considered optimial but not a target of therapy)
|
|
non-HDL
|
Measures cholesterol in all atherogenic lipoproteins Useful to measure when TG is elevated (>4.5 mmol/L) as LDL cannot be calculated |
< 2.6 mmol/L
|
|
TC/HDL-C Ratio
|
Total cholesterol divided by HDL-C. A traditional risk marker that is often high when HDL-C is low and TG are high (typical in diabetes population) Considered when looking at overall CV risk but not a target of therapy.
|
No specified target (Generally >4 is considered elevated but not a target of therapy)
|
|
TG
|
Triglycerides A form of fat that is an important energy source for the body. Usually stored in adipose tissue, TG's will be found in the blood as they move from storage to replenish cells in the body.
|
Not a target for CV risk reduction but <1.5 mmol/L considered optimal
|
|
Drugs to Protect
Diabetes Canada's Reducing Vascular Risk tool (link available on our Topics Catalogue) helps the clinician decide if vascular protective medication is required.
The interactive tool is based on the following algorithm:
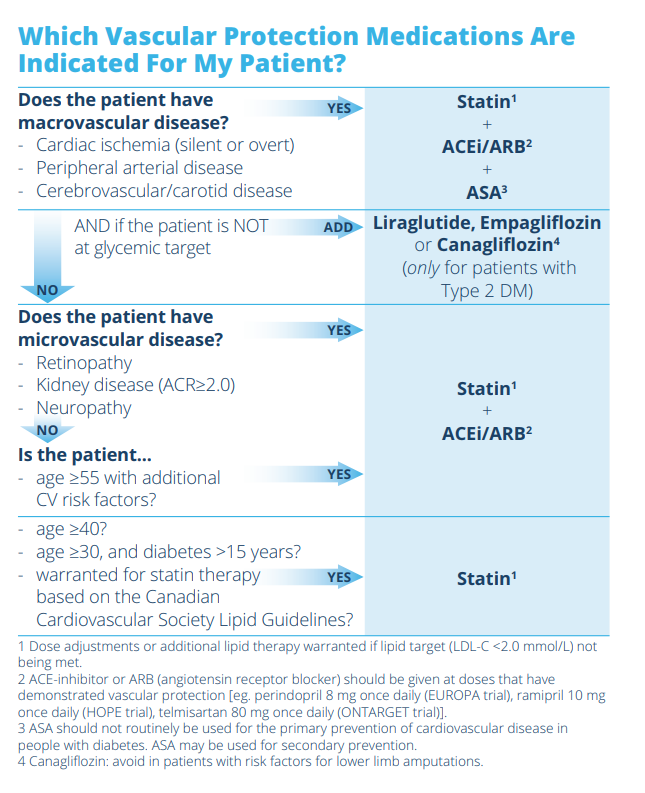
Image Courtesy : Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada. Can J Diabetes. 2018;42(Suppl 1):S1-S325. Accessed July 2018.
Exercise and Healthy Eating
Physical activity and healthy nutrition have both been shown to reduce risk for major adverse cardiovascular events. See our Physical Activity page and Nutrition page for more details.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking cessation is very important for overall health and reducing risk of cardiovascular disease. See the Topics Catalogue: Smoking Cessation for list of resources along with our Smoking Cessation page for more details.
References:
Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada. Can J Diabetes. 2018;42(Suppl 1):S1-S325. Accessed July 2018.
2016 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in the Adult. Can J Cardiology. 2016; 32 (11) : 1263-1282.