This article reviews the basics of continuous glucose monitoring. Please also view the complete list of CGM articles on our Continuous Glucose Monitoring page.
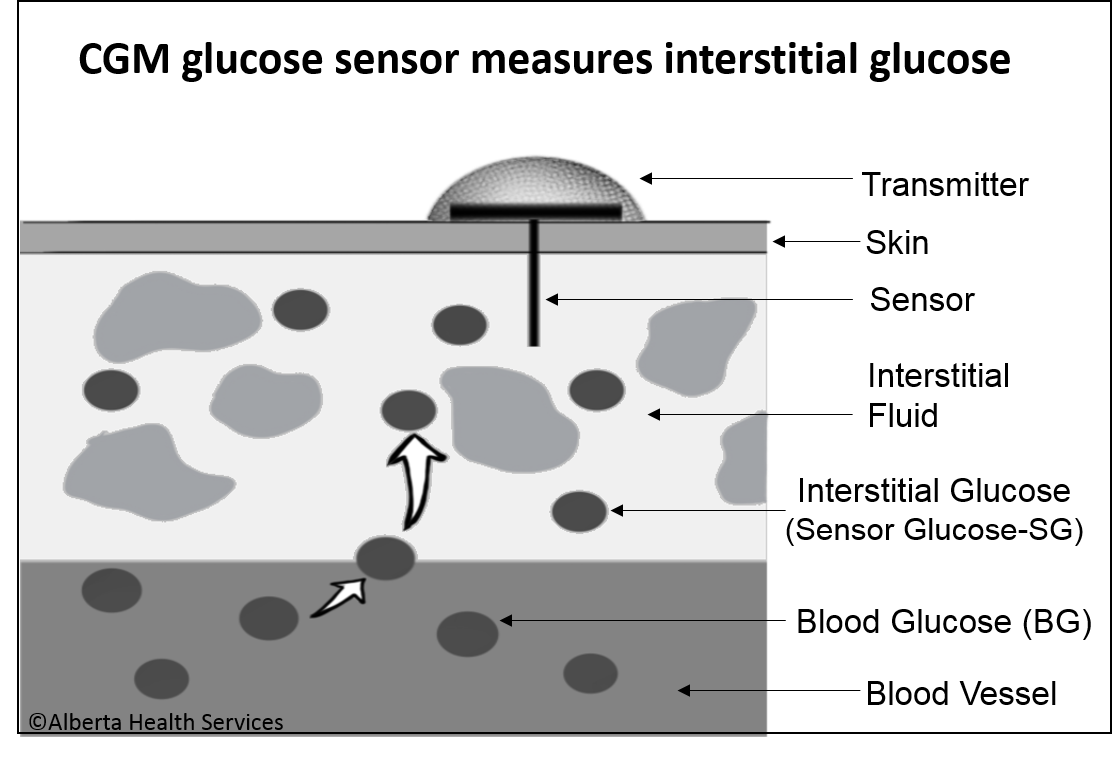
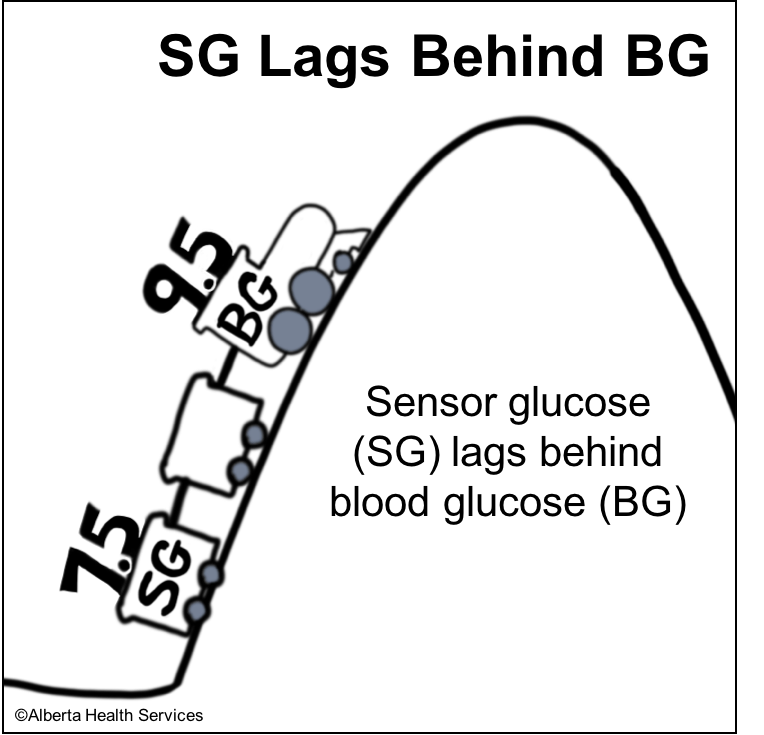
- Interstitial glucose readings are “older” than blood glucose readings by 5-15 minutes. This lag in time varies and can be longer after eating or after treating a low blood sugar. Therefore, CGM results don’t always match fingerstick blood glucose readings.
- A glucose sensor (small electrode) is inserted under the skin and measures interstitial glucose every 1-5 minutes. The readings are sent wirelessly to a device to be viewed.
- Results can also be uploaded to a server (cloud) to create reports for viewing glucose control over longer periods of time.
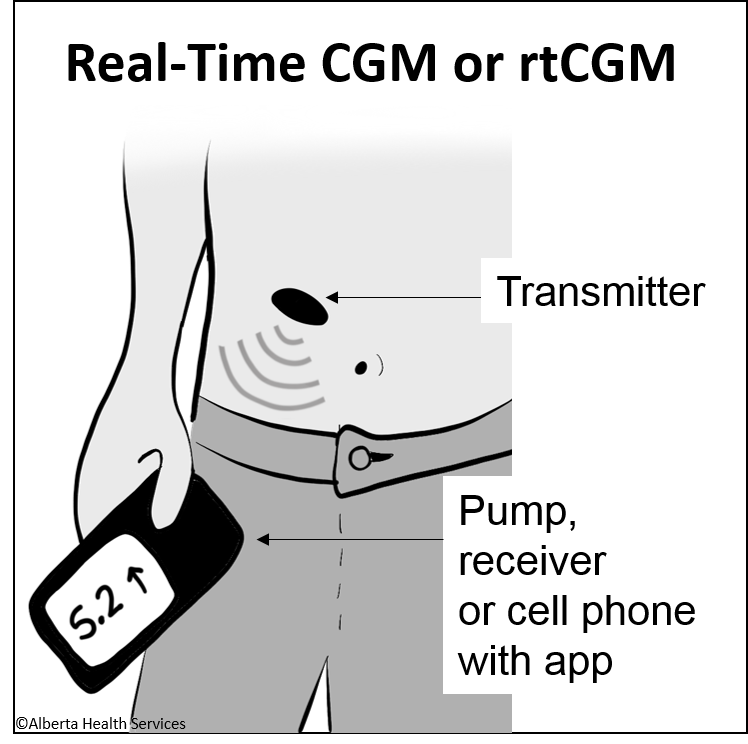
Real Time CGM (rtCGM)
- Current sensors available in the Canadian market are all Real-Time CGMs (rtCGM). This includes Dexcom, Medtronic and also the Libre 2 if it has been upgraded to the newest app. (Libre 1 is not rtCGM. It requires the user to hold a "Reader", that looks like a meter, near the sensor to see the glucose level).
- Results from rtCGMs are sent directly to a phone app and to some insulin pumps. For those without a smart phone, some companies may have a receiver to purchase so results can be viewed.
- Apps alarm when glucose levels reach certain limits or change too quickly. Fingerstick testing is needed to calibrate rtCGMs at least twice daily and at other time
Benefits & Challenges (Brief)
Benefits of CGM may include:
- Improved glycemic control.
- Improved ability to identify glucose patterns and make daily management decisions.
- Less fingerstick glucose testing:
- More information than fingerstick tests:
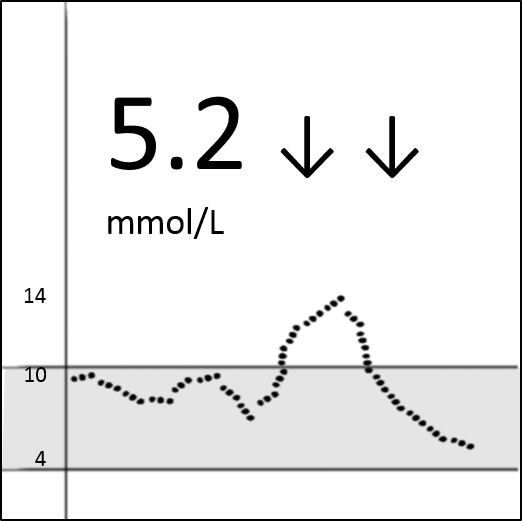
- CGM apps show a current glucose reading, a graph of previous hours’ glucose levels and rate of change (ROC) arrows. More information can lead to different decisions. E.g. A reading of 5.2 mmol/L ↓↓ (dropping quickly) would likely require action to prevent a low, whereas a 5.2 mmol/L → (stable) might not.
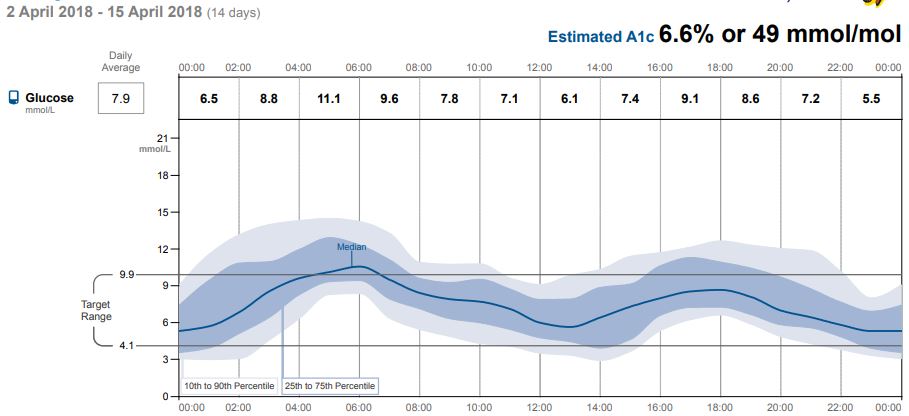
- In Reports: CGM devices offer various reports, including some type of Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP). The AGP translates glucose data into an image to easily identify glucose patterns. The "Dark Blue River" in the AGP below represents 50% of all readings. The "Light Blue River" (between the top and bottom edges of the light blue) contains 80%. A "flatter" and "narrower" river represents more desirable glycemic control.
Challenges of CGM include:
- Cost
- Alarm fatigue, feeling overwhelmed by data (this could lead to too many insulin adjustments)
- Unrealistic expectations
- Skin irritation
- The requirement for fingerstick glucose tests for some situations (all brands).
- Lag time: Sensor glucose (SG) readings can lag behind blood glucose (BG) readings at times, particularly when glucose levels change quickly (after eating, bolusing, treating low blood sugars, exercise).